DDL(数据定义语言)
数据库相关
-- 创建数据库
create database testdb;
-- 更改数据库
alter database testdb rename to mydb;
-- 删除数据库
drop database mydb;表相关
-- 创建表
create table course (
course_id char(4) primary key ,
course_name varchar(20) not null unique ,
course_type varchar(10) null check ( course_type in ('基础课', '专业课', '选修课') ),
course_credit smallint null,
course_period smallint null,
test_method char(4) not null default '闭卷考试'
);
-- 修改表结构
ALTER TABLE student ADD selfinfo varchar(100);
ALTER TABLE student DROP selfinfo;
alter table course rename test_method to exam_method;
alter table course alter column exam_method type char(5);
-- 删除表
drop table course;索引相关
-- 创建索引
create index course_name_idx on course(course_name);
-- 修改索引
alter index course_name_idx rename to c_n_idx;
-- 删除索引
drop index c_n_idx;DML(数据操作语言)
-- 插入数据
insert into course(course_id, course_name, course_type, course_credit, course_period) VALUES
('001', '数据库', '基础课', '4', '36');
insert into course VALUES
('002', '操作系统', '基础课', '4', '36', '闭卷考试');
-- 批量插入数据
insert into course VALUES
('003', 'ARM', '基础课', '4', '36', '闭卷考试'),
('004', '计网', '基础课', '4', '36', '闭卷考试');
-- 更新数据
update course set course_credit=5, course_period=48 where course_name='计网';
-- 删除数据
delete from course where course_name='计网';DQL(数据查询语言)
基础
# 去重
select DISTINCT workaddress as 工作地址 from emp;
# NULL 和 NOT NULL 查询
select * from emp where idcard is null;
select * from emp where idcard is not null;
# BETWEEN ... AND ...
select * from emp where age between 15 and 20;
# in
select * from emp where age in(18, 20, 40);
# LIKE 与 通配符
select * from emp where name like '__';
select * from emp where idcard like '%X';聚合函数
==注意 : NULL值是不参与所有聚合函数运算的。==
# count
select count(*) from emp;
select count(idcard) from emp;
# avg max min
select avg(age) from emp;
select max(age) from emp;
select min(age) from emp;
# sum
select sum(age) from emp where workaddress = '西安';分组查询
where与having区别
- 执行时机不同:where是分组之前进行过滤,不满足where条件,不参与分组;而having是分组 之后对结果进行过滤。
- 判断条件不同:where不能对聚合函数进行判断,而having可以
select gender, count(*) from emp group by gender;
select gender, avg(age) from emp group by gender;
# 查询年龄小于45的员工 , 并根据工作地址分组 , 获取员工数量大于等于3的工作地址
select workaddress, count(*) as address_count from emp where age < 45 group by workaddress having count(*) >= 3;注意事项:
- 分组之后,查询的字段一般为聚合函数和分组字段,查询其他字段无任何意义。
- 执行顺序: where > 聚合函数 > having 。
- 支持多字段分组, 具体语法为 : group by columnA,columnB
排序查询
排序方式 :
-
ASC : 升序(默认值)
-
DESC: 降序
# 升序和降序
select * from emp order by age asc;
select * from emp order by age desc;
select * from emp order by entrydate desc;
# 根据年龄对公司的员工进行升序排序 , 年龄相同 , 再按照入职时间进行降序排序
select * from emp order by age, entrydate desc;
select * from emp order by age asc, entrydate desc;注意事项:
- 如果是升序, 可以不指定排序方式ASC ;
- 如果是多字段排序,当第一个字段值相同时,才会根据第二个字段进行排序 ;
分页查询
在 PostgreSQL 中,您可以使用 LIMIT 和 OFFSET 子句来实现分页查询。LIMIT 用于限制查询结果的数量,OFFSET 用于指定从哪个位置开始返回结果。这里有一个简单的示例:
假设您有一个名为 employees 的数据表,并且您想要查询第 2 页的数据,每页显示 10 条记录。您可以使用以下 SQL 语句实现分页查询:
SELECT * FROM employees
ORDER BY id -- 按照某个字段排序,这里以 id 为例
LIMIT 10 -- 每页显示 10 条记录
OFFSET 10; -- 跳过第一页的 10 条记录,从第 11 条记录开始在这个示例中,我们首先使用 ORDER BY 对结果按照 id 字段进行排序。接着,我们使用 LIMIT 10 限制查询结果为 10 条记录。最后,我们使用 OFFSET 10 跳过第一页的 10 条记录,从第 11 条记录开始返回结果。
您可以根据实际需求调整 LIMIT 和 OFFSET 的值以实现不同的分页查询需求。
由于 PostgreSQL 的分页查询语法与 MySQL 略有不同,以上是 ChatGPT 4.0 的回答,
# 查询第1页员工数据, 每页展示10条记录
select * from emp limit 10 offset 0;
select * from emp limit 10;
# 查询第2页员工数据, 每页展示10条记录
select * from emp limit 10 offset 10;综合练习
-- 查询年龄为20,21,22,23岁的女员工信息
select * from emp where gender = '女' and age in (20, 21, 22, 23);
-- 查询性别为 男 ,并且年龄在 20-40 岁(含)以内的姓名为三个字的员工
select * from emp where gender = '男' and (age between 20 and 40) and name like '___';
-- 统计员工表中, 年龄小于60岁的 , 男性员工和女性员工的人数
select gender, count(*) 人数 from emp where age < 60 group by gender;
-- 查询所有年龄小于等于35岁员工的姓名和年龄,并对查询结果按年龄升序排序,如果年龄相同按入职时间降序排序
select name, age, entrydate from emp where age <= 35 order by age asc, entrydate desc;
-- 查询性别为男,且年龄在20-40 岁(含)以内的前5个员工信息,对查询的结果按年龄升序排序,年龄相同按入职时间升序排序
select * from emp where gender = '男' and (age between 20 and 40) order by age asc, entrydate asc limit 5执行顺序
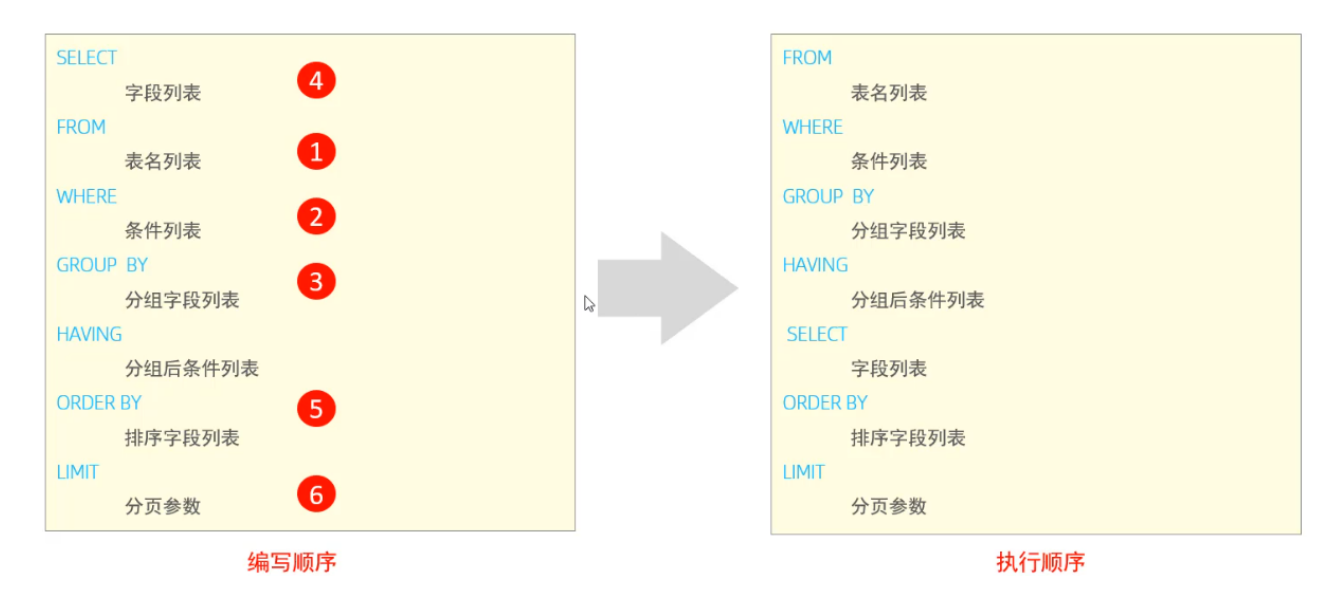
-- from 先于 where 执行,所以 e.age 可以使用
select name, age from emp e where e.age > 15 order by age asc;
-- select 先于 order 执行,所以 eage 可以使用
select name, age eage from emp e where e.age > 15 order by eage asc;DCL(数据控制语言)
create user User_Employee_2021090906016 with
nosuperuser
nocreatedb
nocreaterole
noreplication
login
inherit
connection limit -1
password '123456';
create user User_Admin_2021090906016 with
nosuperuser
nocreatedb
nocreaterole
noreplication
login
inherit
connection limit -1
password '123456';
grant select on Department_2021090906016 to user_employee_2021090906016;
grant select, update on Employee_2021090906016 to user_employee_2021090906016;
grant select on Task_2021090906016 to user_employee_2021090906016;
grant select on Assessment_2021090906016 to user_employee_2021090906016;
revoke select on Department_2021090906016 from user_employee_2021090906016;实测 pgsql 里没有 deny 语句
约束
| 约束 | 描述 | 关键字 |
|---|---|---|
| 非空约束 | 限制该字段的数据不能为null | NOT NULL |
| 唯一约束 | 保证该字段的所有数据都是唯一、不重复的 | UNIQUE |
| 主键约束 | 主键是一行数据的唯一标识,要求非空且唯一 | PRIMARY KEY |
| 默认约束 | 保存数据时,如果未指定该字段的值,则采用默认值 | DEFAULT |
| 检查约束 | 保证字段值满足某一个条件 | CHECK |
| 外键约束 | 用来让两张表的数据之间建立连接,保证数据的一致 性和完整性 | FOREIGN KEY |
注意:约束是作用于表中字段上的,可以在创建表/修改表的时候添加约束。
create table tb_user(
id serial primary key,
name varchar(10) not NULL unique,
age int check(age > 0 AND age <= 120),
status char(1) default '1',
gender char(1)
);
COMMENT ON COLUMN tb_user.id IS 'ID唯一标识';
COMMENT ON COLUMN tb_user.name IS '姓名';
COMMENT ON COLUMN tb_user.age IS '年龄';
COMMENT ON COLUMN tb_user.status IS '状态';
COMMENT ON COLUMN tb_user.gender IS '性别';外键
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept_id foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id);
ALTER TABLE emp DROP CONSTRAINT fk_emp_dept_id;在 PostgreSQL 中,您不能直接删除外键约束,您需要通过删除约束名称来完成此操作
删除/更新行为
添加了外键之后,再删除父表数据时产生的约束行为,我们就称为删除/更新行为。具体的删除/更新行 为有以下几种:
| 行为 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NO ACTION | 当在父表中删除/更新对应记录时,首先检查该记录是否有对应外键,如果有则不 允许删除/更新。 (与 RESTRICT 一致) 默认行为 |
| RESTRICT | 当在父表中删除/更新对应记录时,首先检查该记录是否有对应外键,如果有则不 允许删除/更新。 (与 NO ACTION 一致) 默认行为 |
| CASCADE | 当在父表中删除/更新对应记录时,首先检查该记录是否有对应外键,如果有,则 也删除/更新外键在子表中的记录。 |
| SET NULL | 当在父表中删除对应记录时,首先检查该记录是否有对应外键,如果有则设置子表 中该外键值为null(这就要求该外键允许取null)。 |
| SET DEFAULT | 父表有变更时,子表将外键列设置成一个默认的值 (Innodb不支持) |
-- CASCADE
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id) on delete cascade on update cascade
-- SET NULL
alter table emp add constraint fk_emp_dept foreign key (dept_id) references dept(id) on delete set null on update set null多表查询
多表关系
项目开发中,在进行数据库表结构设计时,会根据业务需求及业务模块之间的关系,分析并设计表结 构,由于业务之间相互关联,所以各个表结构之间也存在着各种联系,基本上分为三种:
- 一对多(多对一)
- 多对多
- 一对一
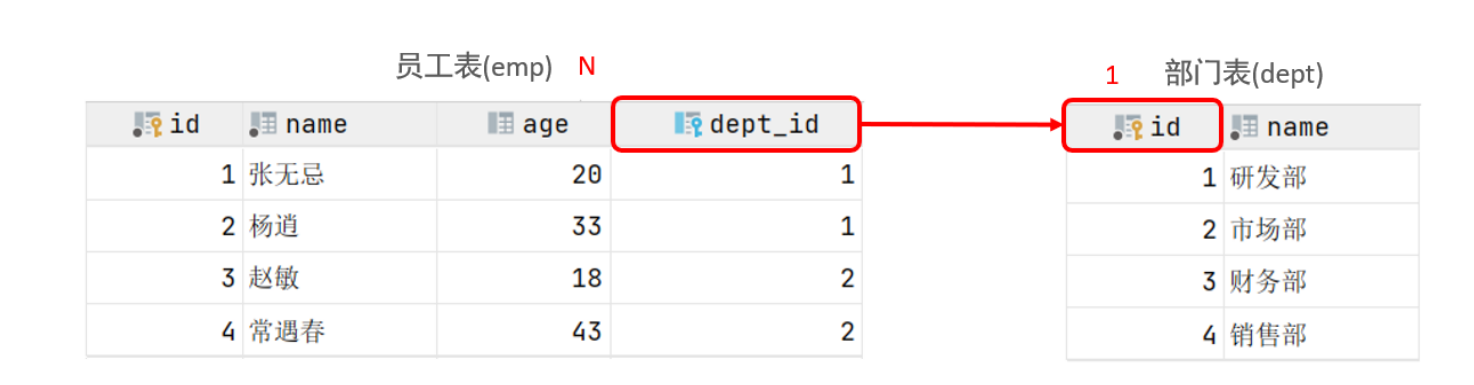
一对多
- 案例: 部门 与 员工的关系
- 关系: 一个部门对应多个员工,一个员工对应一个部门
- 实现: 在多的一方建立外键,指向一的一方的主键
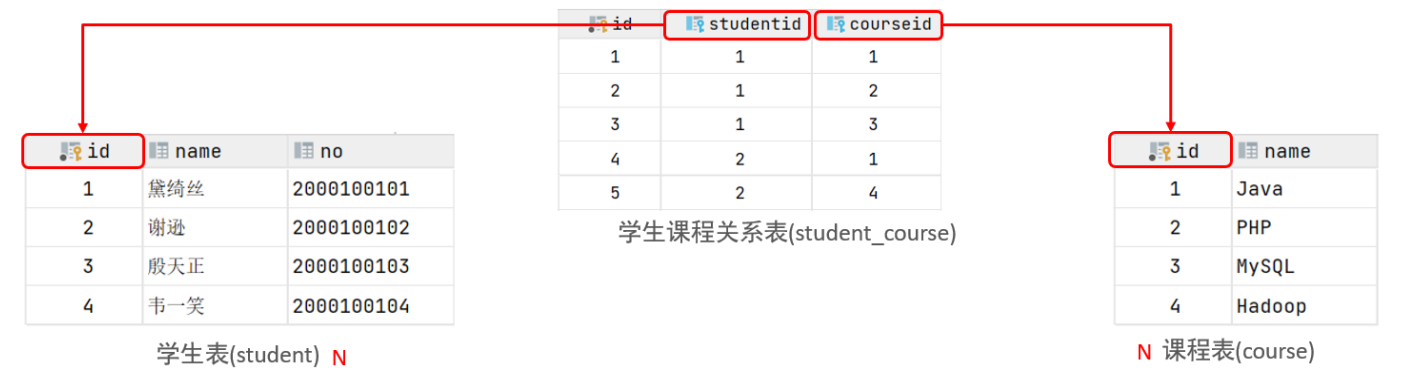
多对多
- 案例: 学生 与 课程的关系
- 关系: 一个学生可以选修多门课程,一门课程也可以供多个学生选择
- 实现: 建立第三张中间表,中间表至少包含两个外键,分别关联两方主键
一对一
- 案例: 用户 与 用户详情的关系
- 关系: 一对一关系,多用于单表拆分,将一张表的基础字段放在一张表中,其他详情字段放在另 一张表中,以提升操作效率
- 实现: 在任意一方加入外键,关联另外一方的主键,并且设置外键为唯一的(UNIQUE)
连接查询
- 连接查询
- 内连接:相当于查询A、B交集部分数据
- 外连接: 左外连接:查询左表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据
- 右外连接:查询右表所有数据,以及两张表交集部分数据
- 自连接:当前表与自身的连接查询,自连接必须使用表别名
-- 多表查询 -- 笛卡尔积
select * from emp, dept;表的别名:
- tablea as 别名1 , tableb as 别名2 ;
- tablea 别名1 , tableb 别名2 ;
注意事项:一旦为表起了别名,就不能再使用表名来指定对应的字段了,此时只能够使用别名来指定字 段。
内连接
-- 隐式内连接(where)
select * from emp, dept where emp.dept_id = dept.id;
select e.name, d.name from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id; /* 起了别名后不能再使用原来的名字 */
-- 显示内连接(inner join)
select e.name, d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
select e.name, d.name from emp e join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;左外连接和右外连接
-- 查询emp表的所有数据, 和对应的部门信息(左外连接)
select e.*, d.name from emp e left outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
-- 查询dept表的所有数据, 和对应的员工信息(右外连接)
select d.*, e.* from emp e right outer join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
-- 右外连接转换为左外连接
select d.*, e.* from dept d left outer join emp e on e.dept_id = d.id;注意事项:左外连接和右外连接是可以相互替换的,只需要调整在连接查询时SQL中,表结构的先后顺 序就可以了。而我们在日常开发使用时,更偏向于左外连接。
自连接
对于自连接查询,可以是内连接查询,也可以是外连接查询。
-- 查询员工及其所属领导的名字
select a.name, b.name from emp a, emp b where a.managerid = b.id;
select a.name, b.name from emp a left join emp b on a.managerid = b.id;注意事项: 在自连接查询中,必须要为表起别名,要不然我们不清楚所指定的条件、返回的字段,到底 是哪一张表的字段。
联合查询
对于union查询,就是把多次查询的结果合并起来,形成一个新的查询结果集。
-- union all, 直接连接(不去重)
select * from emp where salary < 5000
union all
select * from emp where age > 50;
-- union, 去重
select * from emp where salary < 5000
union
select * from emp where age > 50;子查询
标量子查询
子查询返回的结果是单个值(数字、字符串、日期等),最简单的形式,这种子查询称为标量子查询。 常用的操作符:= <> > >= < <=
-- 查询 "销售部" 的所有员工信息
select * from emp where dept_id = (select id from dept where name = '销售部');
-- 查询在 "方东白" 入职之后的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > (select entrydate from emp where name = '方东白')列子查询
常用的操作符:IN 、NOT IN 、 ANY 、SOME 、 ALL
| 操作符 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| IN | 在指定的集合范围之内,多选一 |
| NOT IN | 不在指定的集合范围之内 |
| ANY | 子查询返回列表中,有任意一个满足即可 |
| SOME | 与ANY等同,使用SOME的地方都可以使用ANY |
| ALL | 子查询返回列表的所有值都必须满足 |
-- 查询 "销售部" 和 "市场部" 的所有员工信息
select * from emp where emp.dept_id in (select id from dept where name in ('销售部', '市场部'));
-- 查询比 财务部 所有人工资都高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > all (select salary from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '财务部'));
-- 查询比研发部其中任意一人工资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > any (select salary from emp where dept_id in (select id from dept where name = '研发部'));行子查询
子查询返回的结果是一行(可以是多列),这种子查询称为行子查询。 常用的操作符:= 、<> 、IN 、NOT IN
-- 查询与 "张无忌" 的薪资及直属领导相同的员工信息
select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌';
select * from emp where (salary, managerid) = (12500, 1);
select * from emp where (salary, managerid) = (select salary, managerid from emp where name = '张无忌');表子查询
子查询返回的结果是多行多列,这种子查询称为表子查询。
常用的操作符:IN
-- 查询与 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
-- a.查询 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资
select job, salary from emp where name in ('鹿杖客', '宋远桥');
-- b.查询与 "鹿杖客" , "宋远桥" 的职位和薪资相同的员工信息
select * from emp where (job, salary) in (select job, salary from emp where name in ('鹿杖客', '宋远桥'));
-- 查询入职日期是 "2006-01-01" 之后的员工信息 , 及其部门信息
-- a.入职日期是 "2006-01-01" 之后的员工信息
select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01';
-- b.查询这部分员工, 对应的部门信息
select * from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
select e.*, d.* from (select * from emp where entrydate > '2006-01-01') e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id;
-- 不使用子查询也行,下面是我想到的 SQL
select * from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.entrydate > '2006-01-01';综合练习
-- 1.查询员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息 (隐式内连接)
select e.name , e.age , e.job , d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
-- 2.查询年龄小于30岁的员工的姓名、年龄、职位、部门信息(显式内连接)
select e.name , e.age , e.job , d.name from emp e inner join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age < 30;
-- 3.查询拥有员工的部门ID、部门名称
select distinct d.id , d.name from emp e , dept d where e.dept_id = d.id;
-- 4.查询所有年龄大于40岁的员工, 及其归属的部门名称; 如果员工没有分配部门, 也需要展示出来(外连接)
select e.*, d.name from emp e left join dept d on e.dept_id = d.id where e.age > 40;
-- 5.查询所有员工的工资等级
select e.* , s.grade , s.losal, s.hisal from emp e , salgrade s where e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal;
-- 6.查询 "研发部" 所有员工的信息及工资等级
select t.* from (emp e left join salgrade s on e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal) t join dept on (t.dept_id = dept.id and dept.name = '研发部');
select e.* , s.grade from emp e , dept d , salgrade s where e.dept_id = d.id and (e.salary between s.losal and s.hisal ) and d.name = '研发部';
-- 7.查询 "研发部" 员工的平均工资
select avg(e.salary) from emp e, dept d where e.dept_id = d.id and d.name = '研发部';
-- 8.查询工资比 "灭绝" 高的员工信息。
select * from emp where salary > (select salary from emp where name = '灭绝');
-- 自连接, my answer
select e1.* from emp e1, emp e2 where e2.name = '灭绝' and e1.salary > e2.salary;
-- 9.查询比平均薪资高的员工信息
select * from emp where salary > (select avg(salary) from emp);
-- 10.查询低于本部门平均工资的员工信息
-- my answer
select dept_id, avg(salary) from emp group by dept_id;
select e.*, t.avg from emp e, (select dept_id, avg(salary) avg from emp group by dept_id) t where e.dept_id = t.dept_id and e.salary < t.avg;
-- Jury's answer
select * from emp e2 where e2.salary < ( select avg(e1.salary) from emp e1 where e1.dept_id = e2.dept_id );
-- 11.查询所有的部门信息, 并统计部门的员工人数
-- my answer,存在BUG: 员工数量为0的部门查询不到
select dept_id, count(*) from emp group by dept_id;
select d.*, t.count from dept d, (select dept_id, count(*) from emp group by dept_id) t where d.id = t.dept_id
-- Jury's answer
select d.id, d.name, ( select count(*) from emp e where e.dept_id = d.id ) 人数 from dept d;
-- 12.查询所有学生的选课情况, 展示出学生名称, 学号, 课程名称
select s.name , s.no , c.name from student s , student_course sc , course c where s.id = sc.studentid and sc.courseid = c.id ;
事务
事务 是一组操作的集合,它是一个不可分割的工作单位,事务会把所有的操作作为一个整体一起向系 统提交或撤销操作请求,即这些操作要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
注意: 默认MySQL的事务是自动提交的,也就是说,当执行完一条DML语句时,MySQL会立即隐 式的提交事务。
事务操作
在 PostgreSQL 中,您可以通过 SHOW TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL 查询事务隔离级别以了解事务是否自动提交。以下是将 MySQL 的 SQL 语句转换为 PostgreSQL 支持的 SQL 语句:
SHOW TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL;如果返回的隔离级别是 "READ COMMITTED",那么 PostgreSQL 默认使用自动提交。
begin; /* 或者 start transaction */
-- 1. 查询张三余额
select * from account where name = '张三';
-- 2. 张三的余额减少1000
update account set money = money - 1000 where name = '张三';
-- 3. 李四的余额增加1000
update account set money = money + 1000 where name = '李四';
-- 如果执行过程中报错, 则回滚事务
-- rollback;
-- 如果正常执行完毕, 则提交事务
commit;
-- 恢复
update account set money = 2000 where name = '张三' or name = '李四';注意:上述的这种方式,我们是修改了事务的自动提交行为, 把默认的自动提交修改为了手动提 交, 此时我们执行的DML语句都不会提交, 需要手动的执行commit进行提交。
事务四大特性
- 原子性(Atomicity):事务是不可分割的最小操作单元,要么全部成功,要么全部失败。
- 一致性(Consistency):事务完成时,必须使所有的数据都保持一致状态。
- 隔离性(Isolation):数据库系统提供的隔离机制,保证事务在不受外部并发操作影响的独立 环境下运行。
- 持久性(Durability):事务一旦提交或回滚,它对数据库中的数据的改变就是永久的。
上述就是事务的四大特性,简称ACID。
并发事务问题
- 赃读:一个事务读到另外一个事务还没有提交的数据。
- 不可重复读:一个事务先后读取同一条记录,但两次读取的数据不同,称之为不可重复读。
- 幻读:一个事务按照条件查询数据时,没有对应的数据行,但是在插入数据时,又发现这行数据 已经存在,好像出现了 "幻影"。
事务隔离级别
为了解决并发事务所引发的问题,在数据库中引入了事务隔离级别。主要有以下几种:
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Read uncommitted | 未解决 | 未解决 | 未解决 |
| Read committed(PostgreSQL 默认) | 解决 | 未解决 | 未解决 |
| Repeatable Read(MySQL 默认) | 解决 | 解决 | 未解决 |
| Serializable | 解决 | 解决 | 解决 |
注意:事务隔离级别越高,数据越安全,但是性能越低。
不可重复读 复现示例:
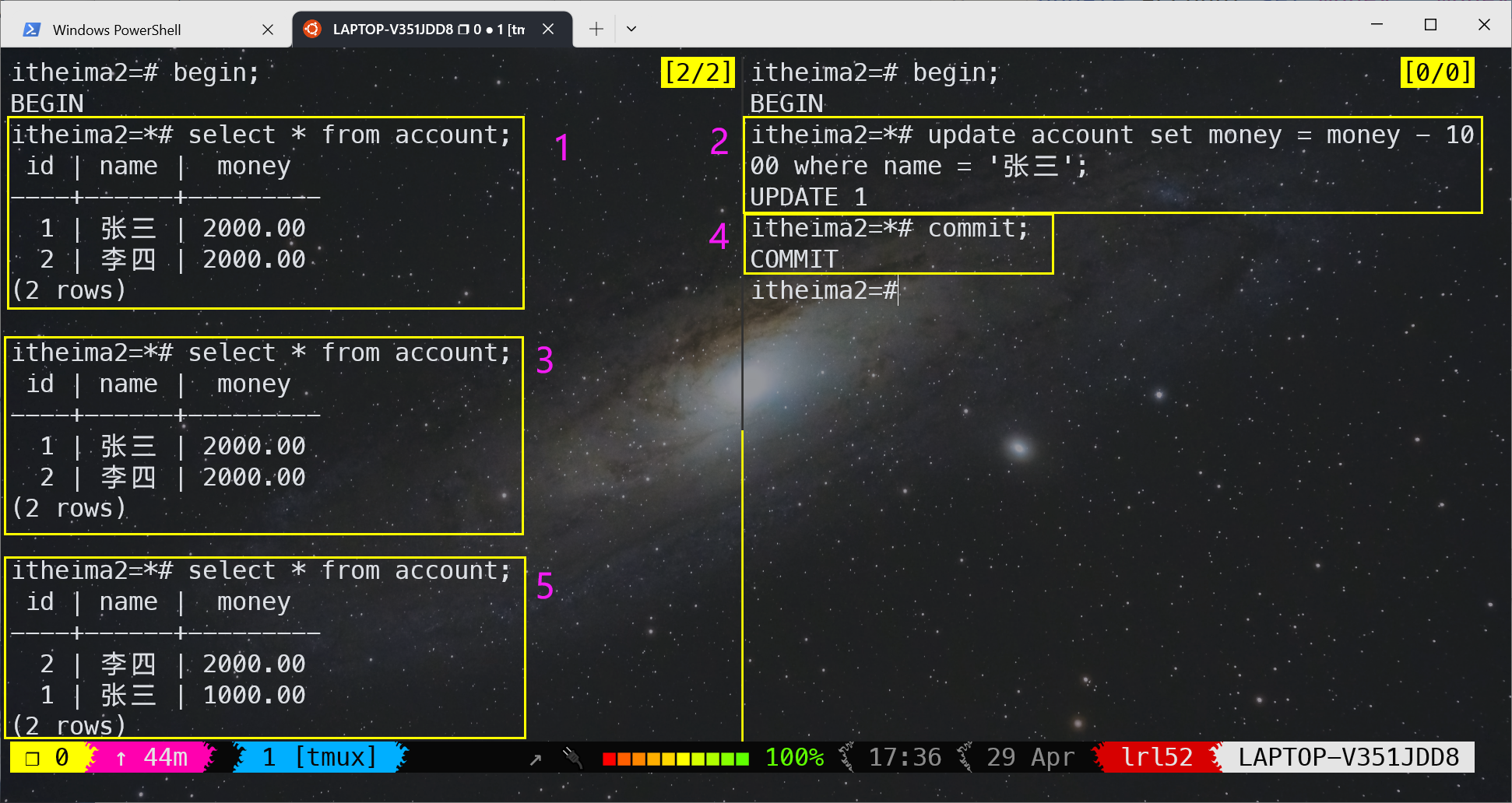
-- 显示当前会话的默认隔离级别
show transaction isolation level ;要更改当前会话的默认隔离级别为 SERIALIZABLE,您可以使用 SET 语句,而不需要在事务中进行设置。以下是将当前会话的默认隔离级别更改为 SERIALIZABLE 的示例:
SET SESSION CHARACTERISTICS AS TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL SERIALIZABLE;在执行此语句后,当前会话中启动的所有新事务将使用 SERIALIZABLE 隔离级别。要查看当前会话的默认隔离级别,您可以使用以下查询:
SHOW default_transaction_isolation;这将返回当前会话的默认隔离级别,如 SERIALIZABLE。
请注意,这里设置的默认隔离级别仅适用于当前会话。当会话结束时,这个设置将失效。如果您想要为整个数据库设置默认的隔离级别,需要更改 postgresql.conf 配置文件中的 default_transaction_isolation 设置,并重启数据库服务。
如果只需要在一次事务中更改隔离级别的话,可以这样写:
BEGIN; -- 开始一个新事务
SET TRANSACTION ISOLATION LEVEL SERIALIZABLE; -- 设置事务隔离级别为 SERIALIZABLE
-- 在这里执行您的事务操作(如查询、插入、更新等)
COMMIT; -- 提交事务视图
视图(View)是一种虚拟存在的表。视图中的数据并不在数据库中实际存在,行和列数据来自定义视 图的查询中使用的表,并且是在使用视图时动态生成的。
通俗的讲,视图只保存了查询的SQL逻辑,不保存查询结果。所以我们在创建视图的时候,主要的工作 就落在创建这条SQL查询语句上。
基本语法
-- 创建视图
create or replace view stu_view as
select id, name from student where id <= 10;
-- 查询视图定义
select pg_get_viewdef('stu_view', true);
select viewname, definition from pg_views where viewname = 'stu_view' and schemaname = 'public';
-- 查询视图
select * from stu_view where id < 3;
-- 修改视图
create or replace view stu_view as select id,name,no from student where id <= 10;
-- 在 PostgreSQL 中,您不能直接修改现有视图的定义,而是需要使用 CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW 语句来重新创建视图
-- alter view stu_view as select id,name from student where id <= 10;
-- 删除视图
drop view if exists stu_view;检查选项
当使用 WITH CHECK OPTION 子句创建视图时,MySQL 会通过视图检查正在更改的每个行,例如 插 入,更新,删除,以使其符合视图的定义。 MySQL 允许基于另一个视图创建视图,它还会检查依赖视 图中的规则以保持一致性。为了确定检查的范围,MySQL 提供了两个选项: CASCADED 和 LOCAL ,默认值为 CASCADED 。
create view v1 as
select id, name from student where id <= 20;
create view v2 as
select id, name from v1 where id >= 10 with cascaded check option ;
insert into v1 values (25, 'pgsql'); /* 成功 */
insert into v2 values (15, 'pgsql'); /* 失败 */
create view v3 as
select id, name from v2 where id >= 5 with local check option ;
insert into v3 values (8, 'pgsql'); /* 失败 */
create or replace view v3 as
select id, name from v1 where id >= 5 with local check option ;
insert into v3 values (8, 'pgsql'); /* 成功 */视图的更新
要使视图可更新,视图中的行与基础表中的行之间必须存在一对一的关系。如果视图包含以下任何一 项,则该视图不可更新:
A. 聚合函数或窗口函数(SUM()、 MIN()、 MAX()、 COUNT()等)
B. DISTINCT
C. GROUP BY
D. HAVING
E. UNION 或者 UNION ALL
视图作用
-
简单
视图不仅可以简化用户对数据的理解,也可以简化他们的操作。那些被经常使用的查询可以被定义为视 图,从而使得用户不必为以后的操作每次指定全部的条件
-
安全
数据库可以授权,但不能授权到数据库特定行和特定的列上。通过视图用户只能查询和修改他们所能见到的数据
-
数据独立
视图可帮助用户屏蔽真实表结构变化带来的影响
存储过程
存储过程是事先经过编译并存储在数据库中的一段 SQL 语句的集合,调用存储过程可以简化应用开发 人员的很多工作,减少数据在数据库和应用服务器之间的传输,对于提高数据处理的效率是有好处的。
存储过程思想上很简单,就是数据库 SQL 语言层面的代码封装与重用。
基本语法
在 PostgreSQL 中,函数(Function)是一种类似于存储过程的可重用对象,它们通常用于封装一组 SQL 语句以执行特定任务、实现复杂的业务逻辑或封装常用操作。与存储过程不同,函数需要返回一个值。您可以使用 PL/pgSQL(一种类似于 SQL 的过程性语言)或其他过程性语言创建函数。
创建函数的基本语法如下:
CREATE [OR REPLACE] FUNCTION function_name (parameter_name parameter_type [,...])
RETURNS return_type
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $$
-- 函数的 PL/pgSQL 代码
$$;其中:
CREATE [OR REPLACE]: 如果指定了OR REPLACE,在创建函数时,如果同名函数已存在,则会用新的定义替换旧的定义。FUNCTION function_name: 函数的名称。parameter_name parameter_type: 函数的输入参数,可以有多个,用逗号分隔。参数有名称和类型。RETURNS return_type: 函数返回值的类型。LANGUAGE plpgsql: 指定函数使用的编程语言。在这里,我们使用 PL/pgSQL。AS $$: 函数的 PL/pgSQL 代码部分的开始。$$;: 函数的 PL/pgSQL 代码部分的结束。
要调用函数,您可以在 SQL 查询中像调用常规函数那样调用它:
SELECT function_name(parameter_values);其中 function_name 是函数的名称,parameter_values 是传递给函数的参数值。
以下是一个简单的函数示例,该函数将两个整数相加并返回结果:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION add_numbers(a INTEGER, b INTEGER)
RETURNS INTEGER
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN a + b;
END;
$$;调用此函数:
SELECT add_numbers(3, 5);这将返回 3 + 5 的结果,即 8。
-- 存储过程基本语法
-- 创建
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION p1()
RETURNS bigint AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN (SELECT count(*) FROM student);
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
-- 调用
select p1();
-- 删除
drop function if exists p1;触发器
触发器是与表有关的数据库对象,指在 insert/update/delete 之前 (BEFORE) 或之后 (AFTER) ,触 发并执行触发器中定义的 SQL 语句集合。触发器的这种特性可以协助应用在数据库端确保数据的完整性 , 日志记录 , 数据校验等操作 。
使用别名 OLD 和 NEW 来引用触发器中发生变化的记录内容,这与其他的数据库是相似的。MySQL 不支持语句级触发,但 PostgreSQL 支持语句级触发。
-- 插入数据触发器
create or replace function tb_user_insert_trigger_function()
returns trigger as $$
begin
insert into user_logs(operation, operate_time, operate_id, operate_params)
values (tg_op, now(), new.id, concat('insert values: ', 'id = ', new.id, ', name = ', new.name, ', phone = ', new.phone, ', email = ', new.email));
return null;
end;
$$ language plpgsql;
create trigger tb_insert_tri
after insert on tb_user for each row
execute function tb_user_insert_trigger_function();
drop trigger if exists tb_insert_tri on tb_user;
insert into tb_user(id, name, phone, email, profession, age, gender, status, createtime)
values (25,'二皇子','18809091212','erhuangzi@163.com','软件工程',23,'1','1',now());
-- 更新数据触发器
create or replace function tb_user_update_trigger_function()
returns trigger language plpgsql as $$
begin
insert into user_logs(operation, operate_time, operate_id, operate_params)
values (tg_op, now(), new.id, concat('old values: ', 'id = ', old.id, ', name = ', old.name, ', phone = ', old.phone, ', email = ', old.email,
' new values: ', 'id = ', new.id, ', name = ', new.name, ', phone = ', new.phone, ', email = ', new.email));
return new;
end;
$$;
create trigger tb_update_tri
after update on tb_user for each row
execute function tb_user_update_trigger_function();
update tb_user set name = 'owo' where id = 25;
-- 删除数据触发器
create or replace function tb_user_delete_trigger_function()
returns trigger language plpgsql as $$
begin
insert into user_logs(operation, operate_time, operate_id, operate_params)
values (tg_op, now(), old.id, concat('delete values: ', 'id = ', old.id, ', name = ', old.name, ', phone = ', old.phone, ', email = ', old.email));
return old;
end;
$$;
create trigger tb_delete_tri
after delete on tb_user for each row
execute function tb_user_delete_trigger_function();
delete from tb_user where id = 25;游标
游标在 PostgreSQL 中是一个数据库查询,它允许你从一个大的结果集中一次获取一行记录。这对于处理大量数据非常有用,因为你不需要一次性加载所有数据。
在 PostgreSQL 中,游标通常在 PL/pgSQL 代码块(如函数或存储过程)中声明和使用,或者在事务中声明使用
-- 游标案例1
create or replace function cursorDemo()
returns boolean language plpgsql as
$$
declare
emp_cur cursor for select * from emp;
re record;
begin
open emp_cur;
loop
fetch next from emp_cur into re;
exit when not found;
raise notice '%, %', re.name, re.job;
end loop;
close emp_cur;
return true;
end;
$$;
select cursorDemo();
-- 游标案例2
create or replace function cursorDemo2(in str varchar)
returns table(name varchar, job varchar) language plpgsql as
$$
declare
emp_cur refcursor;
re record;
begin
open emp_cur for select * from emp where emp.job = str;
fetch emp_cur into re;
while FOUND loop
name := re.name;
job := re.job;
return next;
fetch emp_cur into re;
end loop;
close emp_cur;
end;
$$;
select * from cursorDemo2('职员');杂项
select now();
SELECT current_time AT TIME ZONE 'Asia/Shanghai';
show time zone ;
SHOW config_file;
SET TIME ZONE 'Asia/Shanghai';备份与恢复
在 PostgreSQL 中,备份通常使用 pg_dump 或 pg_dumpall 命令行工具进行,而不是通过 SQL 语句。
例如,你可以使用以下命令来备份一个名为 "sample" 的数据库:
pg_dump sample > sample.bak这个命令将创建一个包含 "sample" 数据库所有数据和结构的 SQL 文件 "sample.bak"。
如果你想备份所有数据库,你可以使用 pg_dumpall 命令:
pg_dumpall > alldbs.bak这个命令将创建一个包含所有数据库的 SQL 文件 "alldbs.bak"。
请注意,这些命令需要在命令行中运行,而不是在 SQL 查询中。你可能需要具有适当的权限才能运行这些命令,具体取决于你的 PostgreSQL 安装和配置。

