终于来到了传说中的 COW fork 实验,关于 COW 这个机制,已经无数次听学长和同学谈起,也是面试重点,我同学孟爷爷曾经面试 ysyx 夏令营就被问到过 COW。自己也曾尝试了解 Linux 内核中的 COW 实现,是时候终于自己亲手实现一下 COW 了。
这个 Lab 不需要额外花时间看 textbook 和 Xv6 代码,因此上手很快,是用时最短的 Lab。同时由于这个 Lab 也是我 debug 时间最长的 Lab,是我做 Xv6 Lab 以来第一个遇到的感到 debug 无从下手的 Lab。
Lab5
由于这是一篇笔记,我就尽量不展示错误代码了,因此先总结一下这个 Lab 里最大的坑:refcount 记着上锁,这个 Lab 会有并发控制挑战,但是整个 Lab 文档的 Hint 竟然没有一点提示,这是令我不解的😇。
页面引用计数(Page Refcount)
这部分的代码都修改于 kalloc.c。
在 Linux 内核中,有 struct page 数据结构来对应每一个 page 的 metadata。在 Xv6 中,我定义了一个 _refcount 数组,来表示每个 page 的引用计数,引用计数为 0 表示 page 可以被释放。这里我用了一个锁来保护 _refcount 字段,实际上更轻量的实现可以用原子指令,但我懒得去查原子指令该怎么用了。
#define PAGE_IDX(pa) (((uint64)pa - (uint64)end) >> PGSHIFT)
static int _refcount[RAM_SIZE / PGSIZE];
static struct spinlock _refcount_lock[RAM_SIZE / PGSIZE];
接下来是实现关于 _refcount 部分读取和修改的代码,这部分有点模仿 Linux 内核中的风格,但实际上我自己也觉得实现得很丑。
这里有个让我纠结的地方在于,put_page 会减少引用计数,那么如果引用引用计数为 0 时,是由 put_page 来调用 kfree 释放页面,还是在外面判断,再手动调用 kfree 释放。关于这个问题我特意查看了 Linux 内核代码,内核代码中关于 __free_pages 有这样一段注释:
If you want to use the page’s reference count to decide when to free the allocation, you should allocate a compound page, and use put_page() instead of __free_pages().
翻译过来大致意思就是,如果你想通过 page reference count 来决定什么时候释放页面,那么你应该使用 put_page。也就是说,put_page 会负责释放引用计数为 0 的页面。当然在这个 Lab 中,我不想去更改太多代码,懒得去把原来那些的 kfree 调用换成 put_page 调用。因此在这个 Lab 中,我为了兼容性和鲁棒性,我的 kfree 和 put_page 实现的语义是等价的,他们都会负责检查 refcount,并且仅在 refcount <= 0 时才会释放页面。
// Get the refer ence count of the page
int
get_refcount(void *pa) {
return _refcount[PAGE_IDX(pa)];
}
// Set the reference count of the page
void
set_refcount(void *pa, int count) {
int idx;
idx = PAGE_IDX(pa);
acquire(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
_refcount[idx] = count;
release(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
}
// Increment the reference count
int
page_ref_inc(void *pa) {
int idx, ret;
idx = PAGE_IDX(pa);
acquire(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
ret = ++_refcount[idx];
release(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
return ret;
}
// Decrement the reference count
int
page_ref_dec(void *pa) {
int idx, ret;
idx = PAGE_IDX(pa);
acquire(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
ret = --_refcount[idx];
release(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
return ret;
}
// Increment the reference count of
// the page. This is the same as page_ref_inc.
void
get_page(void *pa) {
page_ref_inc(pa);
}
// Decrement the reference count of
// the page. If the reference count
// falls to 0, free the page.
void
put_page(void *pa) {
if (get_refcount(pa) == 1) {
kfree(pa);
} else {
page_ref_dec(pa);
}
}
Copy-On-Write
我使用 PTE 中的 bit8 来表示这是一个 COW page。
#define PTE_COW (1L << 8) // copy on write
对于 COW,模仿 Linux 内核,定义一个 do_cow_page 函数来处理一个 COW 页面。(hh 实际上定义函数是的目的是代码复用,减少重复代码,提高可维护性,如果 COW 仅在 usertrap 中用到了,那我根本不会去专门写这样一个函数,而是因为在 copyout 中我们也需要用到 do_cow_page 的代码。其实一开始我就没有定义 do_cow_page 函数,后面发现 copyout 需要用才把这部分代码封装成一个函数的)
封装函数,该怎么封装呢?也就是说 do_cow_page 的语义应该是怎样的?一开始我的实现是下面这样的,传入一个 pagetable 和 va 作为参数,表示处理这个 pagetable 下的 va 虚拟地址出的 cow page,这个实现是没有问题的。
// do a copy-on-write page fault.
int
do_cow_page(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 va) {
uint flags;
pte_t *pte;
void *pa1, *pa2;
va = PGROUNDDOWN(va);
pte = walk(pagetable, va, 0);
flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
if ((flags & PTE_COW) == 0) // not a copy-on-write page
return -1;
pa1 = (void*)PTE2PA(*pte);
flags = (flags & ~PTE_COW) | PTE_W;
if (get_refcount(pa1) == 1) {
// optimization: if only one process is using the page,
// we can just change the flags
*pte = CLEAR_FLAGS(*pte) | flags;
} else {
// we need to copy the page, unmap the old page,
// and map the new page
pa2 = kalloc();
if (pa2 == 0)
return -2;
memmove(pa2, pa1, PGSIZE);
uvmunmap(pagetable, va, 1, 1);
if (mappages(pagetable, va, PGSIZE, (uint64)pa2, flags) != 0) {
kfree(pa2);
return -3;
}
}
return 0;
}
但上面这个实现并不够好,里面的 walk 是多余的,处理一个 COW page,仅需要传入这个 va 对应的 PTE 的地址就足够了,uvmunmap 和 mappages的调用也是多余的。(实际上这个想法来自在 usertrap 和 copyout 中调用 do_cow_page 的写代码感受,觉悟出这样修改 do_cow_page 的语义会更有利于代码复用和提高效率)。
修改后的 do_cow_page 的实现是简单而优雅的。在 do_cow_page 时,我有一个优化,如果当前 page 的引用计数是 1,那么就不需要再 Copy-On-Write 了,直接修改页表项删除 PTE_COW,把 PTE_W 置位即可。
// do a copy-on-write page fault.
int
do_cow_page(pte_t *pte) {
uint flags;
void *pa1, *pa2;
flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
pa1 = (void*)PTE2PA(*pte);
flags = (flags & ~PTE_COW) | PTE_W;
if (get_refcount(pa1) == 1) {
// optimization: if only one process is using the page,
// we can just change the flags
*pte = CLEAR_FLAGS(*pte) | flags;
} else {
// we need to copy the page, unmap the old page,
// and map the new page
pa2 = kalloc();
if (pa2 == 0)
return -2;
memmove(pa2, pa1, PGSIZE);
kfree(pa1);
*pte = PA2PTE(pa2) | flags;
}
return 0;
}
修改 usertrap 增加处理 store/AMO page fault 的情况,注意需要判断地址是否在 MAXVA 以内。
//
// handle an interrupt, exception, or system call from user space.
// called from trampoline.S
//
void
usertrap(void)
{
int which_dev = 0, rc;
uint64 va;
uint flags;
pte_t *pte;
if((r_sstatus() & SSTATUS_SPP) != 0)
panic("usertrap: not from user mode");
// send interrupts and exceptions to kerneltrap(),
// since we're now in the kernel.
w_stvec((uint64)kernelvec);
struct proc *p = myproc();
// save user program counter.
p->trapframe->epc = r_sepc();
if(r_scause() == 8){
// system call
if(killed(p))
exit(-1);
// sepc points to the ecall instruction,
// but we want to return to the next instruction.
p->trapframe->epc += 4;
// an interrupt will change sepc, scause, and sstatus,
// so enable only now that we're done with those registers.
intr_on();
syscall();
} else if((which_dev = devintr()) != 0){
// ok
} else if (r_scause() == 15) {
// store/AMO page fault
va = r_stval();
if (va >= MAXVA)
goto KILL;
va = PGROUNDDOWN(va);
pte = walk(p->pagetable, va, 0);
flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
if ((flags & PTE_COW) == 0)
goto KILL;
rc = do_cow_page(pte);
if (rc != 0) {
printf("do_cow_page failed: %d\n", rc);
goto KILL;
}
} else {
KILL:
printf("usertrap(): unexpected scause %p pid=%d\n", r_scause(), p->pid);
printf(" sepc=%p stval=%p\n", r_sepc(), r_stval());
setkilled(p);
}
if(killed(p))
exit(-1);
// give up the CPU if this is a timer interrupt.
if(which_dev == 2)
yield();
usertrapret();
}
uvmcopy 和 copyout
修改 uvmcopy,拷贝父进程时不再无脑分配内存了,
// Given a parent process's page table, copy
// its memory into a child's page table.
// Copies both the page table and the
// physical memory.
// returns 0 on success, -1 on failure.
// frees any allocated pages on failure.
int
uvmcopy(pagetable_t old, pagetable_t new, uint64 sz)
{
pte_t *pte;
uint64 pa, i;
uint flags;
for(i = 0; i < sz; i += PGSIZE){
if((pte = walk(old, i, 0)) == 0)
panic("uvmcopy: pte should exist");
if((*pte & PTE_V) == 0)
panic("uvmcopy: page not present");
pa = PTE2PA(*pte);
flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
// Clear PTE_W in the PTEs of both old and new
// and set PTE_COW in both.
if (flags & PTE_W) {
flags &= ~PTE_W;
flags |= PTE_COW;
*pte = CLEAR_FLAGS(*pte) | flags;
}
if(mappages(new, i, PGSIZE, pa, flags) != 0){
goto err;
}
get_page((void*)pa);
}
return 0;
err:
uvmunmap(new, 0, i / PGSIZE, 1);
return -1;
}
在 copyout 中,也可能遇到 copyout 的用户程序地址是一个 COW page,因此这部分需要额外处理下 COW 情况,我们直接找到 PTE,然后复用 do_cow_page 即可,
// Copy from kernel to user.
// Copy len bytes from src to virtual address dstva in a given page table.
// Return 0 on success, -1 on error.
int
copyout(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 dstva, char *src, uint64 len)
{
uint64 n, va0, pa0;
pte_t *pte;
while(len > 0){
va0 = PGROUNDDOWN(dstva);
if(va0 >= MAXVA)
return -1;
pte = walk(pagetable, va0, 0);
if(pte == 0 || (*pte & PTE_V) == 0 || (*pte & PTE_U) == 0)
return -1;
if (*pte & PTE_COW) {
if (do_cow_page(pte) != 0)
return -1;
}
if ((*pte & PTE_W) == 0)
return -1;
pa0 = PTE2PA(*pte);
n = PGSIZE - (dstva - va0);
if(n > len)
n = len;
memmove((void *)(pa0 + (dstva - va0)), src, n);
len -= n;
src += n;
dstva = va0 + PGSIZE;
}
return 0;
}
测试
我在 cowtest 中的 three 测试点过不去卡了很久,这个测试点会 fork 出 3 个进程,并疯狂写入,并且最终在正确实现 COW 的情况下内存才不会爆,否则如果有内存泄露,就会 OOM。
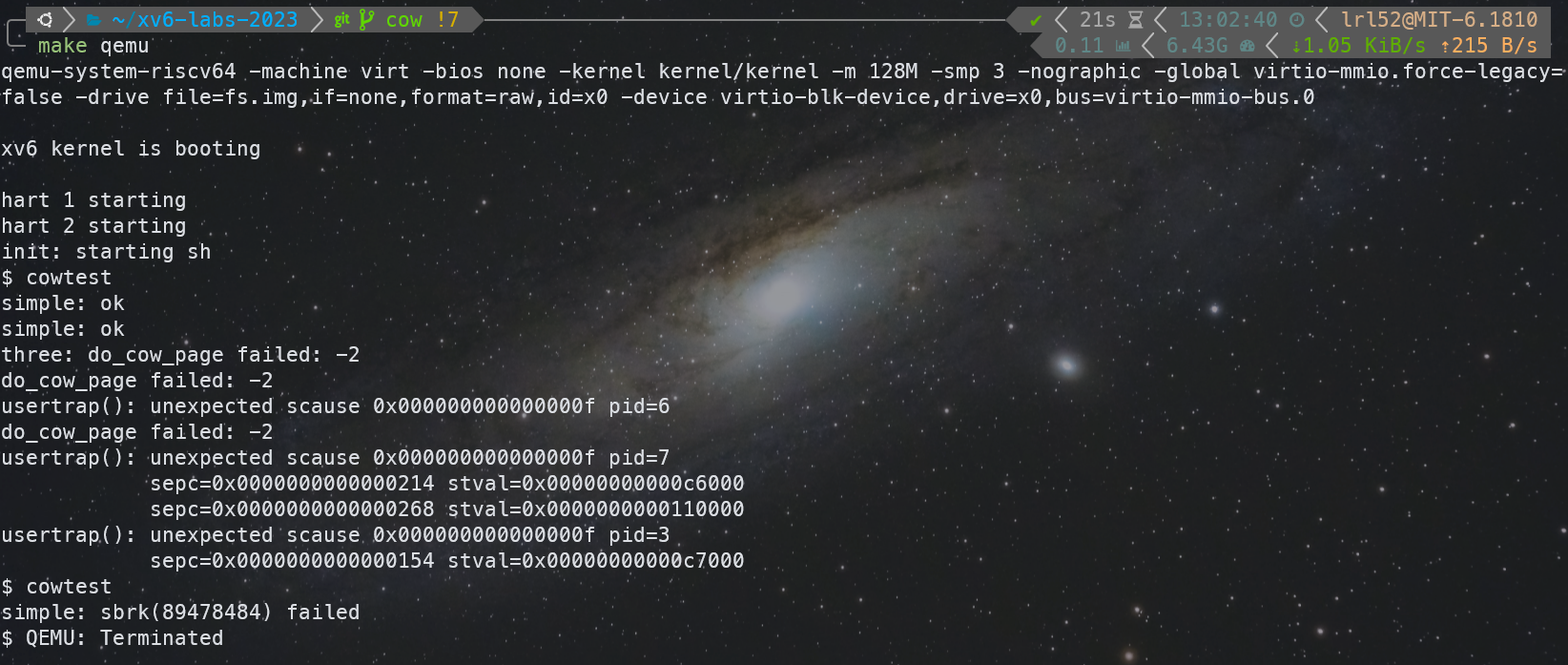
关于这个问题我很难办,因为我想这肯定是发生内存泄露了,但是内存泄露也不好 debug 呀,等 kalloc 失败的时候我也没法找出什么时候内存泄露的,因此在这个问题上我卡了很久,百思不得其解我的代码为什么会内存泄露,并且我在 Xv6 里面加了很多调试代码,这里笔记就不展示了,可以从我的 GitHub 仓库的 commit 中找到。后来在一次调试中,我无意发现,等了很久调试输出语句输出完了之后,我竟然发现我得到了 ALL COW TESTS PASSED。我瞬间明白这是一个并发 BUG,于是我换用 CPUS=1 和 CPUS=2 来跑,发现我都可以通过。

这个并发 BUG 我想很久,最终靠想象力找到了,在kfree 里,原来的错误实现如下(在之前的错误代码里,page_ref_dec 不会返回新值,文章上面展示的代码已经是修复后的正确代码了),在 page_ref_dec 后调用 get_refcount,这中间不是原子的,这期间可能有另外一个进程也 page_ref_dec 了相同的 pa,最后可能导致同一个 pa 被 kfree 了两次,连续kfree 同一个 page 两次后,内核中的空闲内存 page 链表就会形成自环,造成更多不可预测的后果。
page_ref_dec(pa);
if (get_refcount(pa) > 0) {
return;
// panic("kfree: refcount > 0");
}
修复这个困扰了我几个小时的 BUG 后,还有一个小 BUG,这个修复就很简单了,
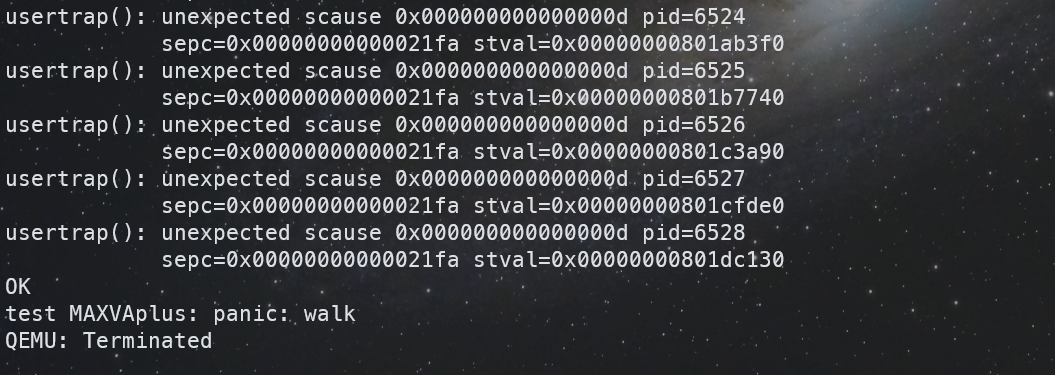
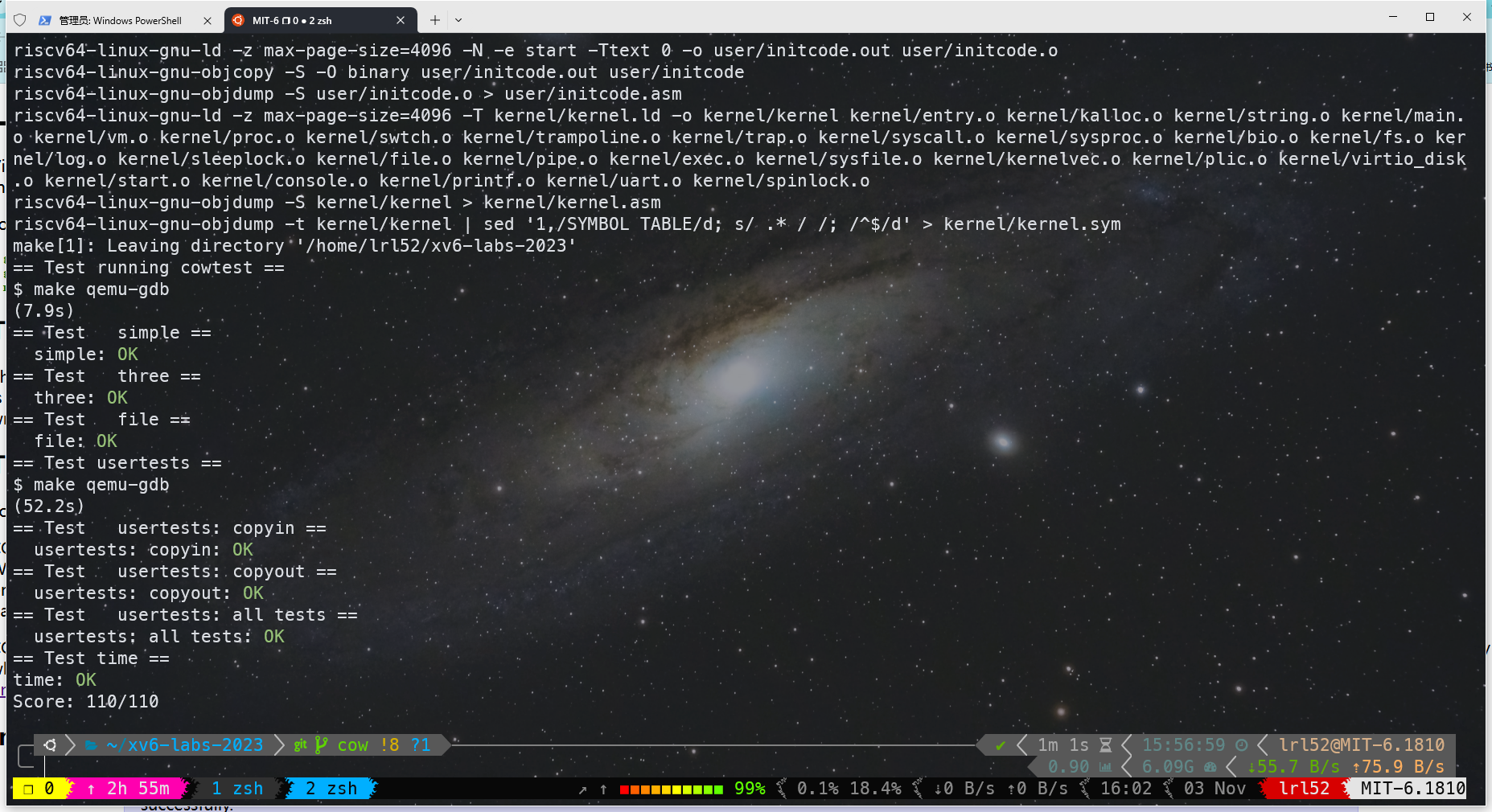
最后测试结果如下:
代码
完整代码如下:
diff --git a/kernel/defs.h b/kernel/defs.h
index a3c962b..c36b3c6 100644
--- a/kernel/defs.h
+++ b/kernel/defs.h
@@ -63,6 +63,12 @@ void ramdiskrw(struct buf*);
void* kalloc(void);
void kfree(void *);
void kinit(void);
+int get_refcount(void *);
+void set_refcount(void *, int);
+int page_ref_inc(void *);
+int page_ref_dec(void *);
+void get_page(void *);
+void put_page(void *);
// log.c
void initlog(int, struct superblock*);
@@ -168,6 +174,7 @@ int uvmcopy(pagetable_t, pagetable_t, uint64);
void uvmfree(pagetable_t, uint64);
void uvmunmap(pagetable_t, uint64, uint64, int);
void uvmclear(pagetable_t, uint64);
+int do_cow_page(pte_t *);
pte_t * walk(pagetable_t, uint64, int);
uint64 walkaddr(pagetable_t, uint64);
int copyout(pagetable_t, uint64, char *, uint64);
diff --git a/kernel/kalloc.c b/kernel/kalloc.c
index 0699e7e..40ed14e 100644
--- a/kernel/kalloc.c
+++ b/kernel/kalloc.c
@@ -14,6 +14,10 @@ void freerange(void *pa_start, void *pa_end);
extern char end[]; // first address after kernel.
// defined by kernel.ld.
+#define PAGE_IDX(pa) (((uint64)pa - (uint64)end) >> PGSHIFT)
+static int _refcount[RAM_SIZE / PGSIZE];
+static struct spinlock _refcount_lock[RAM_SIZE / PGSIZE];
+
struct run {
struct run *next;
};
@@ -26,7 +30,13 @@ struct {
void
kinit()
{
+ int i;
+
initlock(&kmem.lock, "kmem");
+ for (i = 0; i < RAM_SIZE / PGSIZE; ++i) {
+ initlock(&_refcount_lock[i], "_refcount");
+ _refcount[i] = 0;
+ }
freerange(end, (void*)PHYSTOP);
}
@@ -39,6 +49,67 @@ freerange(void *pa_start, void *pa_end)
kfree(p);
}
+// Get the reference count of the page
+int
+get_refcount(void *pa) {
+ return _refcount[PAGE_IDX(pa)];
+}
+
+// Set the reference count of the page
+void
+set_refcount(void *pa, int count) {
+ int idx;
+
+ idx = PAGE_IDX(pa);
+ acquire(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
+ _refcount[idx] = count;
+ release(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
+}
+
+// Increment the reference count
+int
+page_ref_inc(void *pa) {
+ int idx, ret;
+
+ idx = PAGE_IDX(pa);
+ acquire(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
+ ret = ++_refcount[idx];
+ release(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
+ return ret;
+}
+
+// Decrement the reference count
+int
+page_ref_dec(void *pa) {
+ int idx, ret;
+
+ idx = PAGE_IDX(pa);
+ acquire(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
+ ret = --_refcount[idx];
+ release(&_refcount_lock[idx]);
+ return ret;
+}
+
+// Increment the reference count of
+// the page. This is the same as page_ref_inc.
+void
+get_page(void *pa) {
+ page_ref_inc(pa);
+}
+
+// Decrement the reference count of
+// the page. If the reference count
+// falls to 0, free the page.
+void
+put_page(void *pa) {
+ if (get_refcount(pa) == 1) {
+ kfree(pa);
+ } else {
+ page_ref_dec(pa);
+ }
+}
+
+
// Free the page of physical memory pointed at by pa,
// which normally should have been returned by a
// call to kalloc(). (The exception is when
@@ -50,6 +121,9 @@ kfree(void *pa)
if(((uint64)pa % PGSIZE) != 0 || (char*)pa < end || (uint64)pa >= PHYSTOP)
panic("kfree");
+
+ if (page_ref_dec(pa) > 0)
+ return;
// Fill with junk to catch dangling refs.
memset(pa, 1, PGSIZE);
@@ -76,7 +150,9 @@ kalloc(void)
kmem.freelist = r->next;
release(&kmem.lock);
- if(r)
+ if(r) {
memset((char*)r, 5, PGSIZE); // fill with junk
+ set_refcount((void*)r, 1);
+ }
return (void*)r;
}
diff --git a/kernel/memlayout.h b/kernel/memlayout.h
index cac3cb1..e1debb7 100644
--- a/kernel/memlayout.h
+++ b/kernel/memlayout.h
@@ -42,7 +42,8 @@
// for use by the kernel and user pages
// from physical address 0x80000000 to PHYSTOP.
#define KERNBASE 0x80000000L
-#define PHYSTOP (KERNBASE + 128*1024*1024)
+#define RAM_SIZE 128*1024*1024L
+#define PHYSTOP (KERNBASE + RAM_SIZE)
// map the trampoline page to the highest address,
// in both user and kernel space.
diff --git a/kernel/riscv.h b/kernel/riscv.h
index 20a01db..cbbffd7 100644
--- a/kernel/riscv.h
+++ b/kernel/riscv.h
@@ -343,6 +343,7 @@ typedef uint64 *pagetable_t; // 512 PTEs
#define PTE_W (1L << 2)
#define PTE_X (1L << 3)
#define PTE_U (1L << 4) // user can access
+#define PTE_COW (1L << 8) // copy on write
// shift a physical address to the right place for a PTE.
#define PA2PTE(pa) ((((uint64)pa) >> 12) << 10)
@@ -351,6 +352,8 @@ typedef uint64 *pagetable_t; // 512 PTEs
#define PTE_FLAGS(pte) ((pte) & 0x3FF)
+#define CLEAR_FLAGS(pte) ((pte) & ~0x3FF)
+
// extract the three 9-bit page table indices from a virtual address.
#define PXMASK 0x1FF // 9 bits
#define PXSHIFT(level) (PGSHIFT+(9*(level)))
diff --git a/kernel/trap.c b/kernel/trap.c
index 512c850..01f35d5 100644
--- a/kernel/trap.c
+++ b/kernel/trap.c
@@ -36,7 +36,10 @@ trapinithart(void)
void
usertrap(void)
{
- int which_dev = 0;
+ int which_dev = 0, rc;
+ uint64 va;
+ uint flags;
+ pte_t *pte;
if((r_sstatus() & SSTATUS_SPP) != 0)
panic("usertrap: not from user mode");
@@ -67,7 +70,27 @@ usertrap(void)
syscall();
} else if((which_dev = devintr()) != 0){
// ok
+ } else if (r_scause() == 15) {
+ // store/AMO page fault
+
+ va = r_stval();
+ if (va >= MAXVA)
+ goto KILL;
+
+ va = PGROUNDDOWN(va);
+ pte = walk(p->pagetable, va, 0);
+ flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
+ if ((flags & PTE_COW) == 0)
+ goto KILL;
+
+ rc = do_cow_page(pte);
+
+ if (rc != 0) {
+ printf("do_cow_page failed: %d\n", rc);
+ goto KILL;
+ }
} else {
+ KILL:
printf("usertrap(): unexpected scause %p pid=%d\n", r_scause(), p->pid);
printf(" sepc=%p stval=%p\n", r_sepc(), r_stval());
setkilled(p);
diff --git a/kernel/vm.c b/kernel/vm.c
index 5c31e87..0688f6a 100644
--- a/kernel/vm.c
+++ b/kernel/vm.c
@@ -315,7 +315,6 @@ uvmcopy(pagetable_t old, pagetable_t new, uint64 sz)
pte_t *pte;
uint64 pa, i;
uint flags;
- char *mem;
for(i = 0; i < sz; i += PGSIZE){
if((pte = walk(old, i, 0)) == 0)
@@ -324,13 +323,17 @@ uvmcopy(pagetable_t old, pagetable_t new, uint64 sz)
panic("uvmcopy: page not present");
pa = PTE2PA(*pte);
flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
- if((mem = kalloc()) == 0)
- goto err;
- memmove(mem, (char*)pa, PGSIZE);
- if(mappages(new, i, PGSIZE, (uint64)mem, flags) != 0){
- kfree(mem);
+ // Clear PTE_W in the PTEs of both old and new
+ // and set PTE_COW in both.
+ if (flags & PTE_W) {
+ flags &= ~PTE_W;
+ flags |= PTE_COW;
+ *pte = CLEAR_FLAGS(*pte) | flags;
+ }
+ if(mappages(new, i, PGSIZE, pa, flags) != 0){
goto err;
}
+ get_page((void*)pa);
}
return 0;
@@ -352,6 +355,33 @@ uvmclear(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 va)
*pte &= ~PTE_U;
}
+// do a copy-on-write page fault.
+int
+do_cow_page(pte_t *pte) {
+ uint flags;
+ void *pa1, *pa2;
+
+ flags = PTE_FLAGS(*pte);
+ pa1 = (void*)PTE2PA(*pte);
+ flags = (flags & ~PTE_COW) | PTE_W;
+ if (get_refcount(pa1) == 1) {
+ // optimization: if only one process is using the page,
+ // we can just change the flags
+ *pte = CLEAR_FLAGS(*pte) | flags;
+ } else {
+ // we need to copy the page, unmap the old page,
+ // and map the new page
+ pa2 = kalloc();
+ if (pa2 == 0)
+ return -2;
+ memmove(pa2, pa1, PGSIZE);
+ kfree(pa1);
+ *pte = PA2PTE(pa2) | flags;
+ }
+
+ return 0;
+}
+
// Copy from kernel to user.
// Copy len bytes from src to virtual address dstva in a given page table.
// Return 0 on success, -1 on error.
@@ -366,8 +396,13 @@ copyout(pagetable_t pagetable, uint64 dstva, char *src, uint64 len)
if(va0 >= MAXVA)
return -1;
pte = walk(pagetable, va0, 0);
- if(pte == 0 || (*pte & PTE_V) == 0 || (*pte & PTE_U) == 0 ||
- (*pte & PTE_W) == 0)
+ if(pte == 0 || (*pte & PTE_V) == 0 || (*pte & PTE_U) == 0)
+ return -1;
+ if (*pte & PTE_COW) {
+ if (do_cow_page(pte) != 0)
+ return -1;
+ }
+ if ((*pte & PTE_W) == 0)
return -1;
pa0 = PTE2PA(*pte);
n = PGSIZE - (dstva - va0);
References
Linux 5.15.19 Source Code
